To the laser related glossary
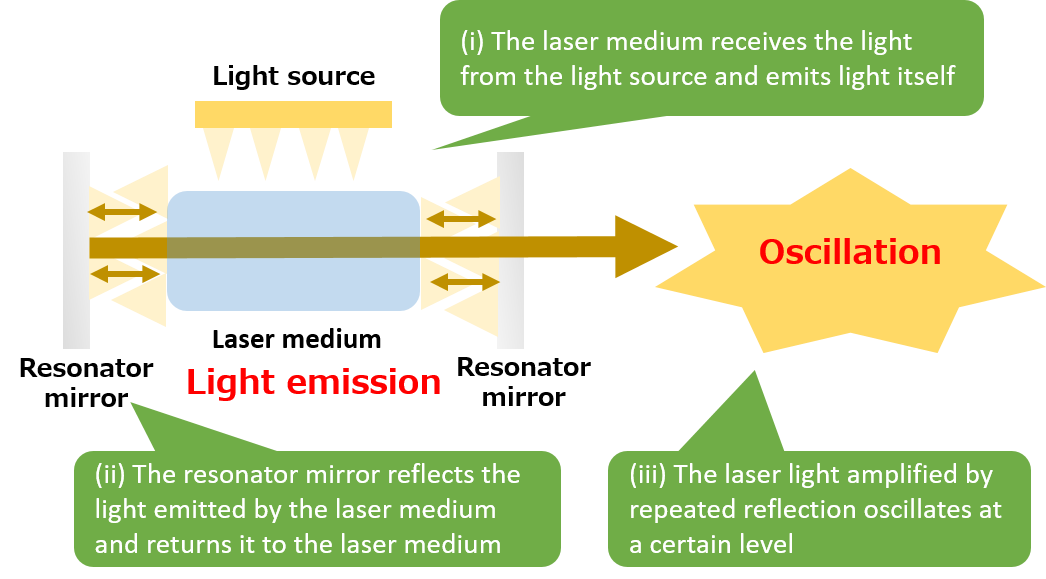
What is laser?

Outline of laser

- LASER
Types of lasers

Lasers are classified into solid, semiconductor, gas, liquid, and chemical lasers according to the type of the laser medium.
Below are the explanations of solid-state lasers and semiconductor lasers.
| Solid-state laser | A solid-state laser is a laser using a solid matter as the laser medium, and as its power is strong with more atoms contained in its volume than a gas laser, used in a variety of fields such as laser machining, laser welding, and laser marking. |
|---|---|
|
Semiconductor laser (LD:Laser Diode) |
A semiconductor laser is a laser using semiconductor as the laser medium. Part of the electric current, when applied to a semiconductor, is converted into light. It is used for various uses taking advantage of the following four features: (i) Small and light (ii) Can be driven at a low voltage/low current, and oscillate easily (iii) Can obtain high conversion efficiency as electricity is directly converted into light (iv) Lasers of various wavelengths can be prepared by changing the composition of semiconductors |
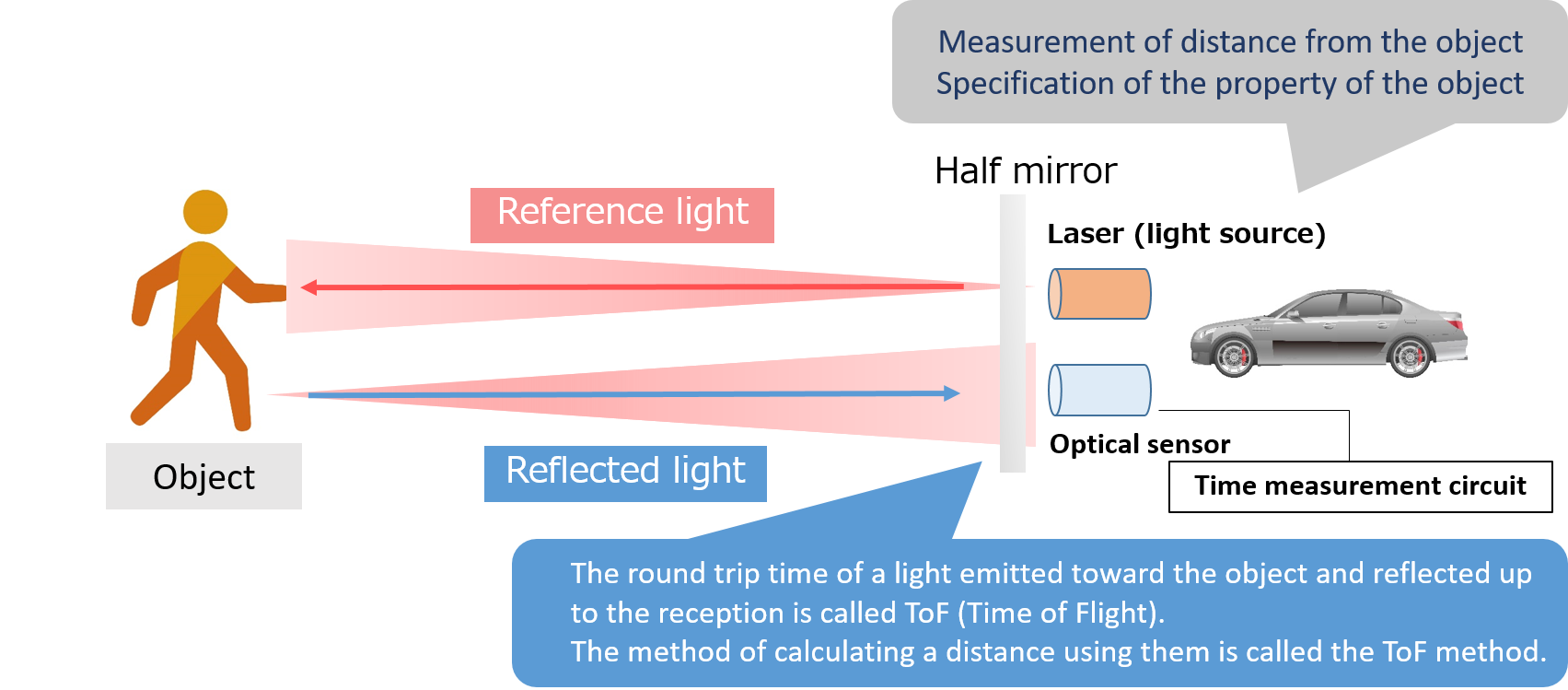
Explanation by laser use

- LiDAR
| Measurement range comparison | 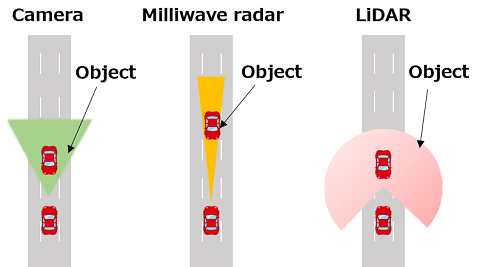 |
|---|---|
| Camera |
- Can identify the object by processing the image taken - Low detection capability in bad weather such as dense fog, heavy rain, and heavy snowfall, in addition to night and backlit conditions. |
|
Milliwave radar (Radar:Radio detection and ranging) |
- Can measure the direction of and the distance of/to the obstacles even at night or in bad weather as it uses electric waves - Has difficulty in detection of small objects and objects with low reflectivity such as corrugated cardboard and expanded polystyrene |
| LiDAR | - Can detect the obstacle distances and relative positions with a high degree of accuracy regardless of the electric wave reflectivity - Can detect small objects as it uses light having a shorter wavelength than millimeter wave radar's - Decreased detection capacity in bad weather, more expensive than millimeter wave radars |
- 5G communications system
- 5G communications infrastructure
| What is 5G? |
It refers to the "5th Generation" (5th Generation Mobile Communication System), the latest communication system succeeding 4G (LTE), which is currently playing the main part of mobile communication. To realize 5G, the following four points are required: (i) High speed and large capacity: Can handle traffic of 20 times or a larger amount than the present (to realize the baud rate at 10 Gbps or above) |
|---|
| Communication system | Transmission rate | Number of simultaneous connections | Delay speed | To process large capacity data, it is necessary to improve the whole infrastructure for speeding up the transmission and reception of devices and elements including semiconductor lasers |
| 5G | 20Gbps at most | 1 mil. units within 1k㎡ | 1ms | |
| 4G | 1Gbps at most | 100 thousand units within 1k㎡ | 10ms |
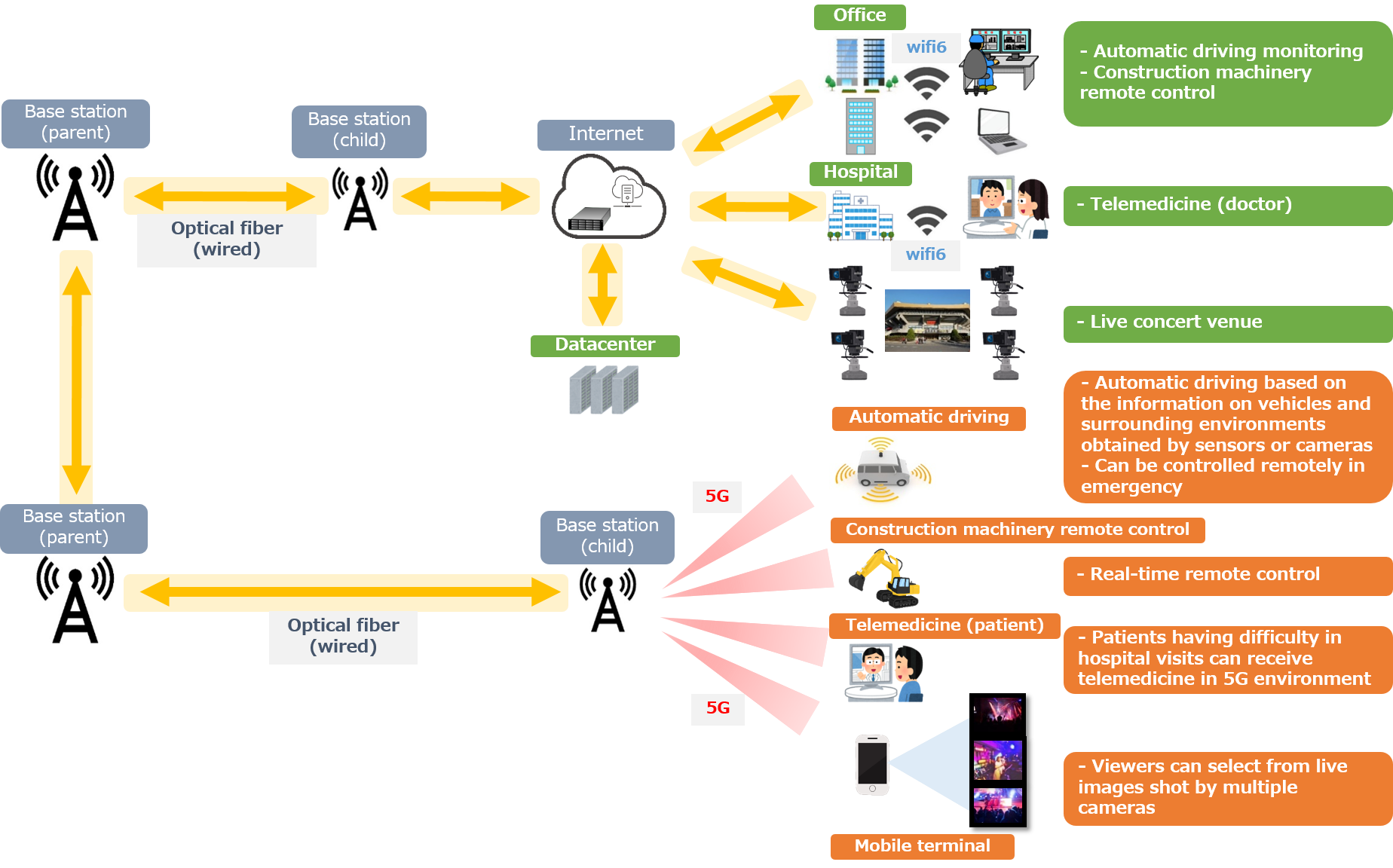
- Laser application to realize 5G communication
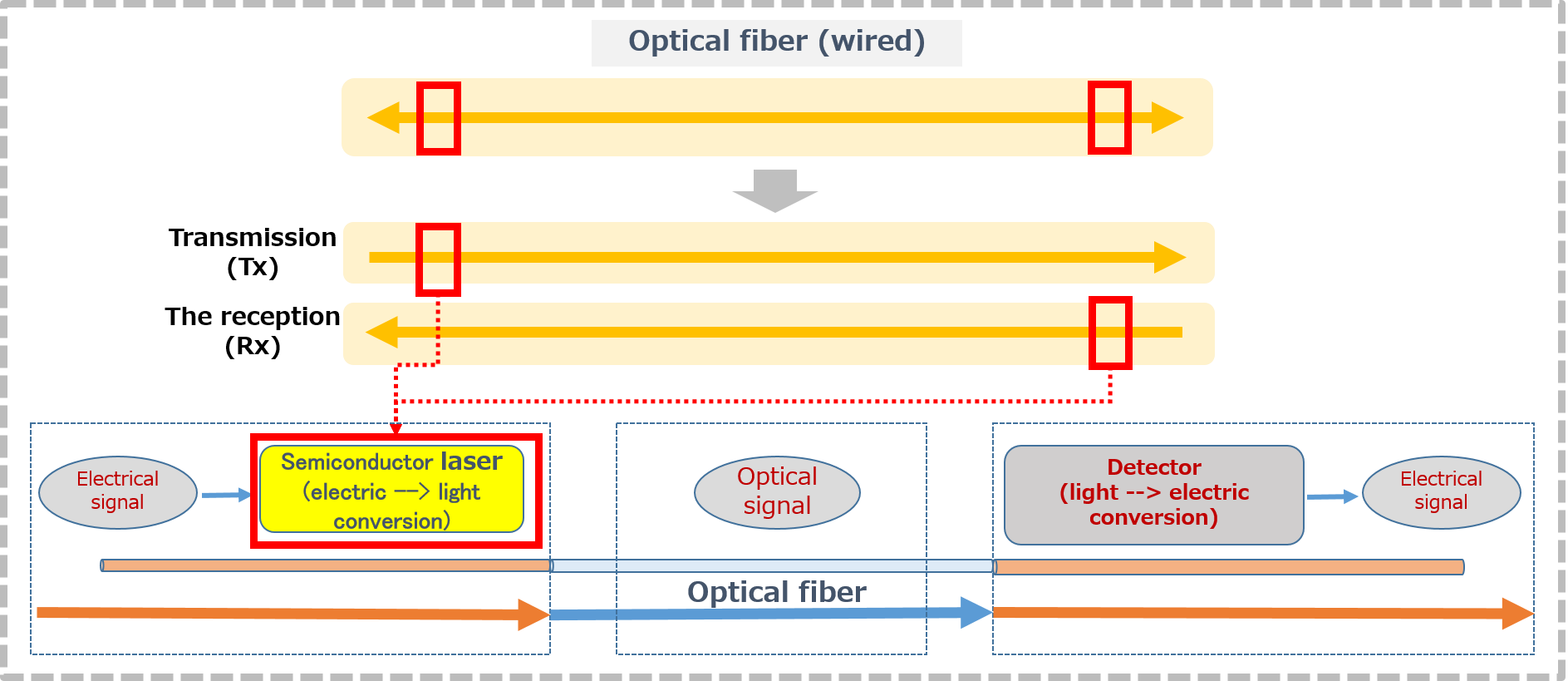
| Laser application | A semiconductor laser converts the electrical signal into light and an optical fiber transmits the laser beam to a distance at high speed with a small loss. |
|---|
- Illumination source
- Laser application for illumination sources
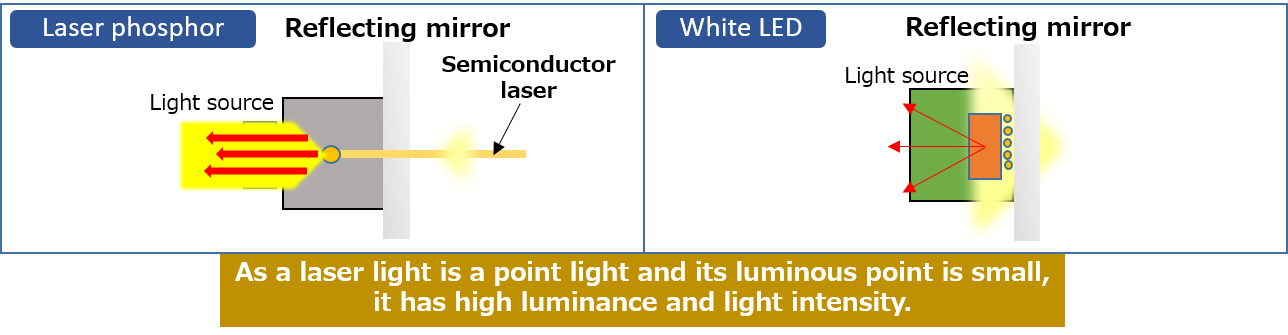
| Laser/LED comparison | Both laser and LED are based on the same principle of including white light emission by applying an electric current to a semiconductor. Their device structures are basically the same. |
|---|---|
| Laser application | Below are main lighting applications: - General lighting: Fluorescent lamp - Special lighting: Car headlight (dedicated to high beam) - Display light source: TV, projector, etc. |